## Analysis: UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s Visit to the US and Request for Security Guarantees for Ukraine
Introduction
The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has drawn significant international attention, with many countries playing crucial roles in diplomatic efforts to resolve the crisis. Recently, UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer visited the United States, where he met with President Donald Trump. A key aspect of their discussions was likely the situation in Ukraine, with the UK seeking to encourage the US to provide stronger security guarantees to Ukraine.
Background: Russia-Ukraine Conflict
The Russia-Ukraine conflict began in 2014 and escalated significantly in February 2022 when Russia launched a large-scale invasion of Ukraine. The conflict has resulted in thousands of casualties, widespread destruction, and a significant humanitarian crisis. The international community, including the UK and the US, has been involved in efforts to support Ukraine through economic sanctions against Russia and military aid to Ukraine.
UK-US Bilateral Relations
The UK and the US have a long-standing “special relationship” characterized by strong defense, security, and trade ties. Both countries are NATO allies and permanent members of the United Nations Security Council, which positions them as key players in global security matters. The UK has been a strong supporter of Ukraine, providing military aid and advocating for increased international pressure on Russia.
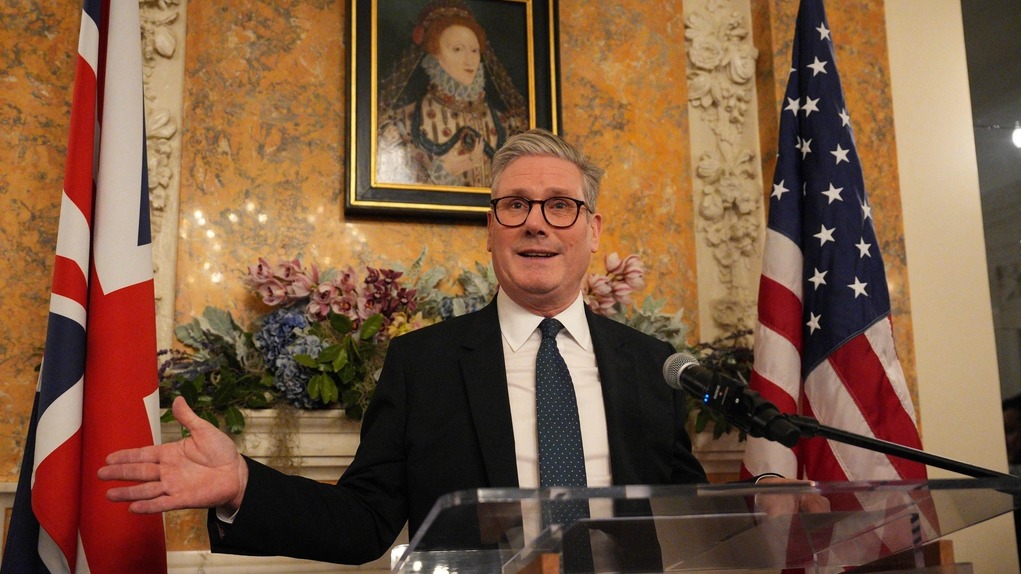
Keir Starmer’s Visit to the US
During his visit, Prime Minister Keir Starmer likely emphasized the importance of the US providing security guarantees to Ukraine. This could involve increased military aid, diplomatic support, or other forms of assistance to help Ukraine defend itself against Russian aggression. The UK’s Labour Party has consistently supported Ukraine and views the US as an indispensable ally in this effort.
Request for Security Guarantees
The request for security guarantees is part of a broader strategy to bolster Ukraine’s defenses and deter further Russian aggression. The US has been a major provider of military aid to Ukraine, and any additional commitments would significantly enhance Ukraine’s ability to resist Russian forces. This move would also underscore the strength of the US-UK alliance in supporting shared security goals.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the strong alliance between the UK and the US, there are challenges in securing additional security guarantees. The US has its own strategic priorities and domestic political considerations that could influence its willingness to commit further resources. Additionally, any significant increase in military aid could escalate tensions with Russia, potentially leading to further conflict.
Conclusion
Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s visit to the US highlights the ongoing efforts by the UK and its allies to support Ukraine in the face of Russian aggression. The request for the US to provide stronger security guarantees to Ukraine reflects the critical role that both countries play in maintaining global security and stability. As the conflict continues, international cooperation will remain essential in achieving a peaceful resolution.
—
Detailed Report
#
Executive Summary
This report provides an analysis of UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s recent visit to the United States, focusing on his discussions with President Donald Trump regarding the Russia-Ukraine conflict. The key objective of the visit was to encourage the US to provide stronger security guarantees to Ukraine, enhancing its ability to defend against Russian aggression.
#
Introduction
The Russia-Ukraine conflict has been a major geopolitical issue since 2014, with significant escalation in 2022. The international community, particularly the UK and the US, has been actively involved in supporting Ukraine through various means.
#
UK-US Bilateral Relations
The UK and the US enjoy a “special relationship” built on strong defense, security, and trade ties. Both countries are key members of NATO and the UN Security Council, positioning them as leaders in global security matters.
#
Keir Starmer’s Visit to the US
During his visit, Prime Minister Starmer emphasized the importance of US support for Ukraine. This included discussions on providing security guarantees, which could involve increased military aid or diplomatic support.
#
Request for Security Guarantees
The request for security guarantees is part of a broader strategy to bolster Ukraine’s defenses. The US has been a major provider of military aid, and additional commitments would significantly enhance Ukraine’s ability to resist Russian forces.
#
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the strong alliance between the UK and the US, there are challenges in securing additional security guarantees. These include strategic priorities, domestic political considerations, and the potential for escalating tensions with Russia.
#
Conclusion
The visit highlights the ongoing efforts by the UK and its allies to support Ukraine. The request for stronger security guarantees reflects the critical role both countries play in maintaining global security and stability.
—
Recommendations for Future Actions
1. Enhanced Military Aid: The US should consider increasing military aid to Ukraine to bolster its defenses against Russian aggression.
2. Diplomatic Support: Both the UK and the US should continue to provide strong diplomatic support to Ukraine, including advocacy within international organizations.
3. International Cooperation: Encourage broader international cooperation to support Ukraine, involving other NATO allies and key global players.
—
Appendix: Key Figures and Organizations Involved
– Keir Starmer: Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
– Donald Trump: President of the United States.
– NATO: North Atlantic Treaty Organization, a key military alliance involving the UK and the US.
– UN Security Council: A primary organ of the United Nations responsible for maintaining international peace and security.
Related sources:
[1] researchbriefings.files.parliament.uk
[2] www.hoover.org
[3] www.politico.eu
[5] www.gov.uk